I am a Ph.D. student working with A/Prof. Luca Cortese and Dr. Amelia Fraser-McKelvie.
My research focus is in the field of extragalactic Astronomy. I study the kinematics of stars and gas in galaxies from the Nearby Universe using Integral-Field Spectroscopic (IFS) data from the SAMI and MaNGA surveys. I am particularly interested in the differences between the rotation of stars and gas as a probe of the processes that shape galaxies throughout their evolution.
My first PhD project focused on the kinematic misalignments between the rotation of stars and gas in the SAMI Galaxy Survey.
Check out the paper on this topic published in MNRAS:
Also have a look at my talks on this topic at ASA ASM 2022 and the ASTRO 3D Science Meeting 2022:
ASTRO 3D 2022:
ASA ASM 2022:
In summary:
- I identified a sample of 169 misaligned galaxies from a total of 1445 galaxies with stellar and gas rotation;
- By combining the spectral properties of misaligned galaxies with their misalignment angle measurement and optical morphology, i identified the most probable physical cause of the kinematic misalignment (see image below; Fig. 6 of paper above);
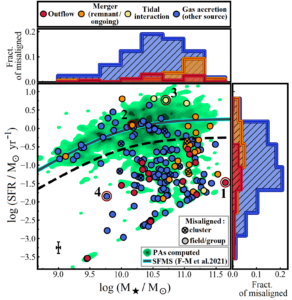
Fig. 6 Causes of kinematic misalignments in the SAMI Galaxy Survey (DR3) shown on the stellar mass-SFR plane.
- The majority of misaligned galaxies have a Low-Ionisation Nuclear Emission Line region (61%) ; 22% have ionisation dominated by star formation while 17% have a significant AGN component (Seyfert objects). For misalignments driven by accretion, the new gas is not feeding new star formation in most cases;
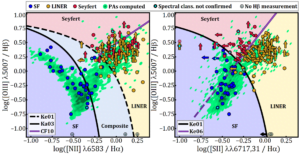
Fig. 4 Spectral classification of misaligned galaxies in SAMI DR3 from the [NII] and [SII] BPT diagrams
- Misaligned galaxies typically have higher Sérsic indices and lower sSFR & stellar spin than appropriately-matched samples of aligned galaxies. This is indicative of the fact that misaligned gas takes longer to precess into a stable configuration in early-type/gas poor galaxies.
I am currently working computing rotation curves for the largest sample of galaxies with IFS observations in the nearby Universe to date, by combining the SAMI and MaNGA Surveys.
Publications:
Social Media:
ICRAR Statement
The content of this page is maintained by Andrei Ristea, please contact them with any questions or comments on this content.